


All of these terms imply change in the direction of the traveling wave due to some interface or obstacle. The black pavement becomes hot from absorbing the light waves and little of the light is reflected making the pavement appear black. In seismic exploration, primarily we are concerned with traveling waves, and the three most important terms which describe wave propagation are reflection, refraction, and diffraction. One example of absorption is black pavement which absorbs energy from light. The wave generally changes the angle of its general direction.
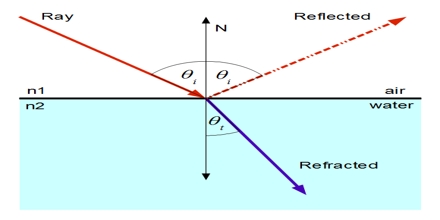
Refraction is when waves, whether physical or electromagnetic, are deflected when the waves go through a substance. A mirror reflects the image of the observer. This vibration absorbs or takes some of the energy away from the wave and less of the energy is reflected. Reflection is when waves, whether physical or electromagnetic, bounce from a surface back toward the source. Reflection Refraction Diffraction Interference Constructive Interference Destructive Interference Doppler effect. Light waves will bend when they interact with an object or traverse a gap. In this picture the unpolarized light wave travels through the filter and then is polarized along a single plane.Ībsorption is when a wave comes into contact with a medium and causes the medium's molecules to vibrate and move. Diffraction is another characteristic of light that resembles a wave. Longitudinal waves, such as sound, cannot be polarized because they always travel in the same direction of the wave. Light waves are often polarized using a polarizing filter. Polarization is when a wave oscillates in one particular direction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
